Data is one of the most important assets of a business, and Data Governance enables us to comply with the regulatory laws related to data. High-quality, structured data allows an organization to get better insights into its business and make necessary changes in the systems to ensure growth. On the other hand, poor-quality data leads to confusion and doesn’t provide a true picture of an organization.
Companies, including small businesses, have realized the importance of data, and they’re investing in tools, technologies, and methodologies that can help them get the most out of this highly valuable asset. In this blog, we’ll discuss data governance — what is it, why it matters, and how to implement it.
What is Data Governance?
There is no simple definition of data governance. It means having policies and standards in place for the effective management of a company’s data across various systems, starting from the point of acquisition till its disposal. It provides answers to the following questions:
- Is the data accurate and reliable?
- Who owns the data?
- Who can access the data and how much?
- What security measures are in place to maintain data privacy?
- Is the data compliant with regulations?
The ultimate goal of data governance is to make sure that the data is accurate, secure, accessible, and usable.
Data Governance vs Data Management
Data governance and data management are often misused interchangeably; however, they are very different from each other. Data governance is an important component of data management that focuses on setting rules and guidelines for the safe collection, use, and accessibility of data throughout its life cycle. Data management, on the other hand, consists of the various processes and technologies used to ingest, store, catalog, and transform a company’s data for analysis and strategic decision-making.
The Need for Data Governance
According to a report by Harvard Business Review, on average, 47% of data records contain critical errors that hamper work. One of the key reasons behind this high percentage of inaccurate data is the lack of good data governance practices in place.
As more and more businesses are considering digital transformation and relying on data analytics to optimize operations, the need for effective data governance has also increased. Virtually all businesses require data governance of some level. But the big question is — why? Let’s find out.
- To Remove Data Inconsistencies – Lack of effective data governance can lead to inconsistencies in data moving across different systems of an organization. For instance, the address of a customer might be listed in different formats across various transaction processing systems, hampering data integration. Data governance allows a company to remove these inconsistencies by implementing common data definitions and standard formats for data collection and processing.
- To Maintain Compliance – Data is subject to various compliance laws and regulations that govern how a company must handle its data. Examples include the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Failing to meet these compliance requirements can have legal implications for a business. Data governance allows companies to have practices in place to maintain compliance and avoid penalties.
- To Ensure Data Quality – Data lacking quality is just documentation with information, which is practically useless to an organization. Missing information and inaccuracies in data, if not identified and addressed, can lead to costly mistakes as well as impact analytics. Robust data governance ensures that the data is up-to-date, complete, and accurate.
- To Maintain Data Security – Data governance also defines who will access what and how much. This accessibility depends on the criticality/sensitivity of the data. Without proper data governance, the security of the data will be compromised. As a business owner, you want to ensure that your data is secure against malicious attacks and protected at all times.
As per GDPR Article 25, companies need to take appropriate measures to ensure that, by default, only personal data, which is necessary for processing, is processed.
Implementation of Data Governance
So, we have understood what data governance is and why businesses need it. Now, let’s discuss how to implement it. The various steps in the process include:
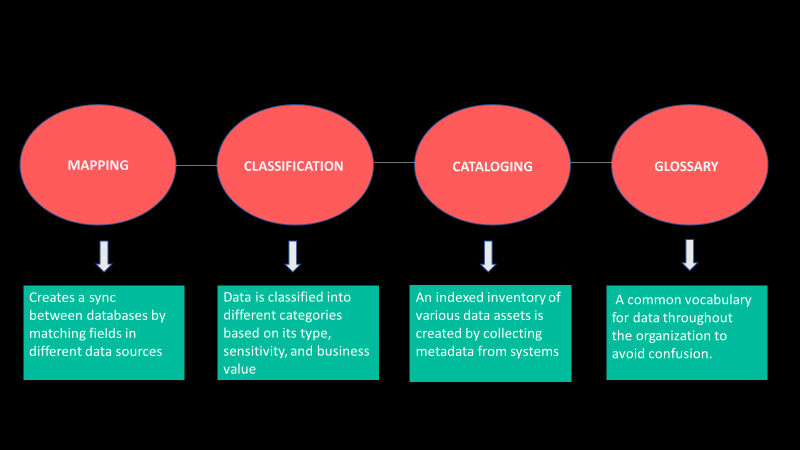
- Data Mapping – As companies collect a large amount of data in multiple formats and databases, there is a need to maintain flow. Data mapping creates a sync between databases by matching fields in different data sources.
- Data Classification – The data needs to be classified into different categories based on its type, sensitivity, and business value. It is a crucial step in data governance as it defines what governance policies will be applied to a data set.
- Data Cataloging – Data cataloging is the process of creating an indexed inventory of various data assets by collecting metadata from systems. This metadata helps data professionals in data discovery and governance. Data cataloging can also be used to index data governance policies and standards to be followed.
- Glossary – A glossary is critical to maintaining consistency and a common vocabulary for data throughout the organization to avoid confusion. It contains various terms and definitions of those terms for a clear understanding of a user or stakeholder in data governance.
Depending on the requirement, a company might opt for a centralized or decentralized data governance model. While a decentralized model is a good choice for individual business owners who manage and maintain their data, a centralized data governance model is better suited to businesses with multiple data owners.
If a company’s data governance strategy involves different departments and divisions, the company can implement the RACI model to clearly define roles for tasks or deliverables for a project or business process, RACI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. The model is an assignment matrix that’s easy to understand and deploy.
Conclusion
Data governance is an extremely important aspect of data management that must not be overlooked. As more and more data are being created, the need to organize and protect it has also increased. With the right data governance strategy in place, businesses can maintain consistency in their data, enhance data quality, improve decision-making and planning, maintain compliance, and increase profitability.
Let Contata be your strategic partner in your journey of digital transformation and suggest ways and solutions so you can better meet your data governance goals.
